Industrial fans are everywhere. We see them in factories, power plants, warehouses, and even inside tunnels. These fans may not seem exciting, but they play a huge role in keeping machines cool, moving air, and making environments safe for workers. Let’s dive into the world of global industrial fan manufacturing technology—with a little fun along the way.
TL;DR
Industrial fans are huge machines used in factories and power plants. They’re made using a mix of smart tech, old manufacturing methods, and tough materials. New tech like AI and smart sensors helps fans work better and use less energy. Plus, new designs are being made to reduce noise and wear.
What Are Industrial Fans?
Simply put, industrial fans move a lot of air. Way more than your living room ceiling fan ever could. They cool equipment, remove harmful fumes, and provide ventilation.
- Axial fans move air in a straight line.
- Centrifugal fans throw air out to the sides like a water sprinkler.
Each type has its own job. But no matter the shape or size, the goal is the same—move air quickly and efficiently.
Materials That Make a Difference
These fans aren’t made of plastic and glue. They’re built to last. Fan parts must handle heat, dust, corrosion, and heavy use.
- Blades – Usually made from aluminum, steel, or composite materials.
- Casings – Often crafted from stainless steel or galvanized iron.
- Motors – The heart of the fan, built for endurance and efficiency.
Some special fans even use coatings to protect against chemicals or high temperatures.
How They’re Made: The Basics
Manufacturing an industrial fan involves both machines and human skills. Here’s a general idea of how it works:
- Designing – Engineers create 3D models using CAD software.
- Cutting – Sheet metal and other materials are laser-cut or punched.
- Shaping – The blades and parts get bent and molded into shape.
- Welding – This joins the parts together with powerful welds.
- Balancing – Blades must be perfectly balanced to avoid wobbling.
- Testing – Every fan undergoes airflow and noise level tests.
Sounds like a big deal, right? It is. A small mistake could mean a noisy or weak fan. Or worse—mechanical failure.
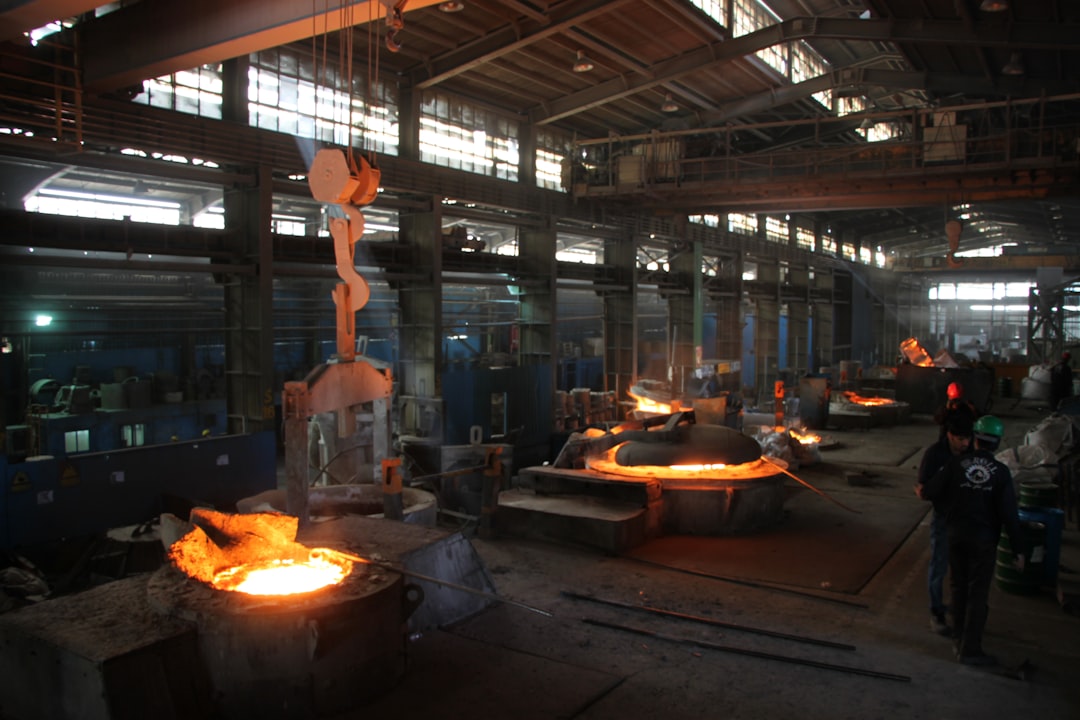

Cool Tech in Fan Manufacturing
Global manufacturing has come far. From manual labor to digital precision, here are some of the coolest tools used:
- CAD Software – Helps design the best shapes for blades and housings.
- CNC Machines – Cut metal perfectly every time.
- 3D Printing – Makes it easy to prototype parts quickly.
- Smart Sensors – Monitor fan performance in real-time.
- IoT Systems – Allow remote control and energy tracking.
Some fans can now “talk” to building systems to adjust speed, temperature, and power use automatically!
Airflow Science: Designing for Performance
Just shaping a blade isn’t enough. Engineers use airflow science to make sure fans do their job properly.
This process includes:
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) – Software to simulate air movement.
- Noise Testing – Making fans quieter through smart designs.
- Blade Angles – Tweaking angle and number of blades for best air volume.
Green Fans: Saving Energy
Energy efficiency is more important than ever. Industrial fans can suck up a lot of power, so manufacturers are working hard to make them greener.
Here’s how they’re doing it:
- Variable Speed Drives – Let fans run at just the right speed.
- EC Motors – Use less energy and generate less heat.
- Smart Controls – Adjust fan output based on real-time data.
In fact, some modern fans use 40% less electricity than older designs! That adds up to big savings over time and a happier planet.
Quality and Safety Checks
You don’t want a 10-foot fan blade flying off during a shift. That’s why safety is non-negotiable.
Every fan goes through:
- Stress Testing – Tests the limits of temperature, vibration, and pressure.
- Run Tests – Simulate real environments for days or even weeks.
- Certifications – ISO standards, OSHA compliance, and CE marks all matter.
These checks ensure fans are safe, strong, and ready to work non-stop.
Global Markets and Leading Players
Fan factories are now using smart technologies all over the world. Some of the biggest players in industrial fan manufacturing are:
- Greenheck (USA)
- ebm-papst (Germany)
- Systemair (Sweden)
- Howden (UK)
- Ziehl-Abegg (Germany)
These companies build fans for factories, ships, tunnels, and even skyscrapers. The competition is fierce, pushing innovation even further.
Customization: Because One Size Doesn’t Fit All
No two industrial settings are the same. That’s why customized fans are a big deal. Manufacturers offer tailored designs based on:
- Airflow needs
- Temperature range
- Size constraints
- Noise limits
- Environmental concerns
This means more 3D modeling, more simulation, and more testing—but the results are high-performance machines built for specific missions.
Challenges in Manufacturing
Of course, it’s not all smooth airflow. Fan makers face some big hurdles:
- Supply Chain Delays – Sourcing metals and motors can take time.
- Rising Costs – Energy and materials aren’t cheap these days.
- Skilled Labor Shortage – Few people are trained in fan-specific tech.
Still, new tools like AI and automation help reduce these pain points bit by bit.

What’s Next for Fan Tech?
The future is blowing in a smart direction! Coming soon to fan manufacturing:
- AI-Powered Maintenance – Predicts failures before they happen.
- Bio-Inspired Designs – Blades shaped like bird wings for better airflow.
- Fully Recyclable Materials – Fans that go green from birth to disposal.
It’s not just flashy tech—it’s about making fans smarter, safer, and more sustainable.
Conclusion
Industrial fans may not be glamorous, but they’re vital to the modern world. From high-tech factories to deep underground tunnels, they keep air moving and machines cool. With new materials, digital tools, and global innovations, fan manufacturing is spinning toward a smarter, greener future. Next time you feel a breeze in a subway or factory, just remember—you’ve got an industrial fan hard at work.
